What is Subject Verb Agreement?
Understanding subject-verb agreement is crucial for efficient communication in English since it is a fundamental part of grammar. if you are a trainer or a teacher, this free PowerPoint presentation on subject-verb agreement will prove to be a timesaver for you. Simply click on the download button and it will automatically download it for you for free.
What are Subject and Verb?
The subject can be either noun or a pronoun. It is always the doer of the action in a sentence. The subject can also be the answer to who or what questions. Ultimately, the subject is the one that experiences the state of being. Verb on the other hand is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being in a sentence. In other words, it is a word that describes an action (such as “run”), a state (such as “be”), or an occurrence (such as “happen”).
The concept of subject-verb agreement is pretty simple. For example, the verb “to be” has the following forms:
- I am
- you are
- He/She/It is
- We are
- They are
If you look at each of these phrases, you will notice that all of them have one subject and one verb, and depending on the subject, the verb form changes. This is what subject-verb agreement means. If the form of the subject changes, the form of the verb also changes. Subject-verb agreement is an important aspect of English grammar because it helps ensure that sentences are clear and easy to understand.
Basic Rule
So, the basic rule of subject-verb agreement is that if the subject is singular, the verb form will also have to be singular. Similarly, if we use a plural subject, then the verb form will also have to be plural.
Exceptions
Either-Or and Neither-Nor Rule
The “either/or” rule in subject-verb agreement applies when the subject of a sentence includes two nouns or pronouns joined by the coordinating conjunction “either…or”.

According to the rule, when the two nouns or pronouns joined by “either…or” are singular, the verb that follows should also be singular. On the other hand, when the two nouns or pronouns are plural, the verb should be plural as well.
It’s important to remember that the verb should agree with the closest noun or pronoun to the verb. In this example, “Students” is the closest noun to the verb “are”, so the verb is plural even though “Sarah” is singular.
And Rule

The “and” rule in subject-verb agreement is used when the subject of a sentence includes two or more nouns or pronouns joined by the coordinating conjunction “and”.
In this example, Sarah and John both are singular nouns; however, when we use and join them together, they became plural nouns. So, the verb changed to a plural verb.
Collective Noun Rule
The general rule for subject-verb agreement with collective nouns is that if the collective noun is considered as a single unit, then it is treated as a singular noun and takes a singular verb. On the other hand, if the collective noun refers to the members of the group acting as individuals, then it is treated as a plural noun and takes a plural verb.
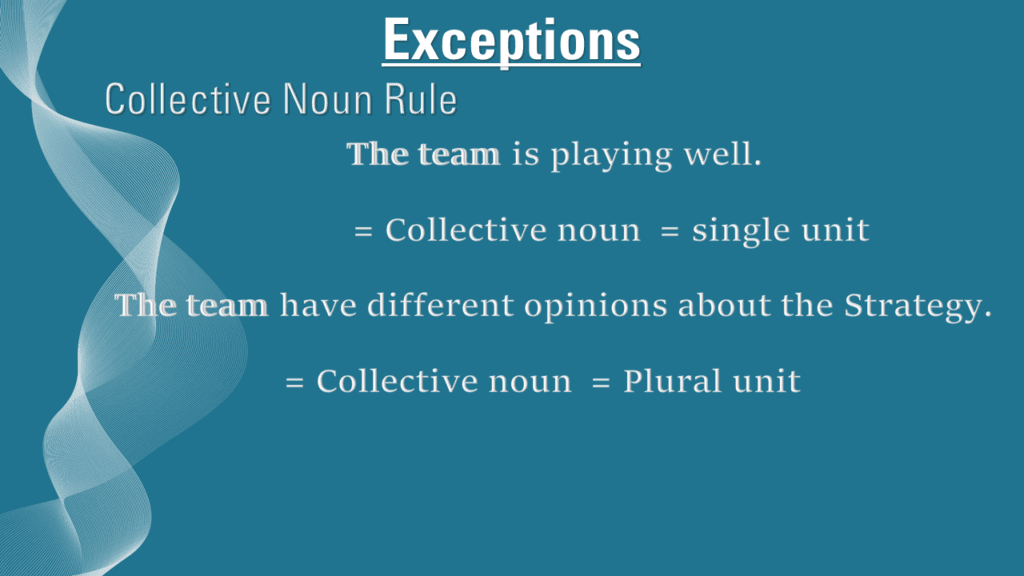
Let me share an example. The team is playing well. In this example, the subject “The Team” is a collective noun and refers to a single team; therefore, the verb used in this sentence is singular. However, if we look at another example, the team have different opinions about the strategy. In this example, the team is considered plural because we are talking about the different opinions of different team members within the team. Therefore, the verb used in this sentence is also plural.
Here and There rule
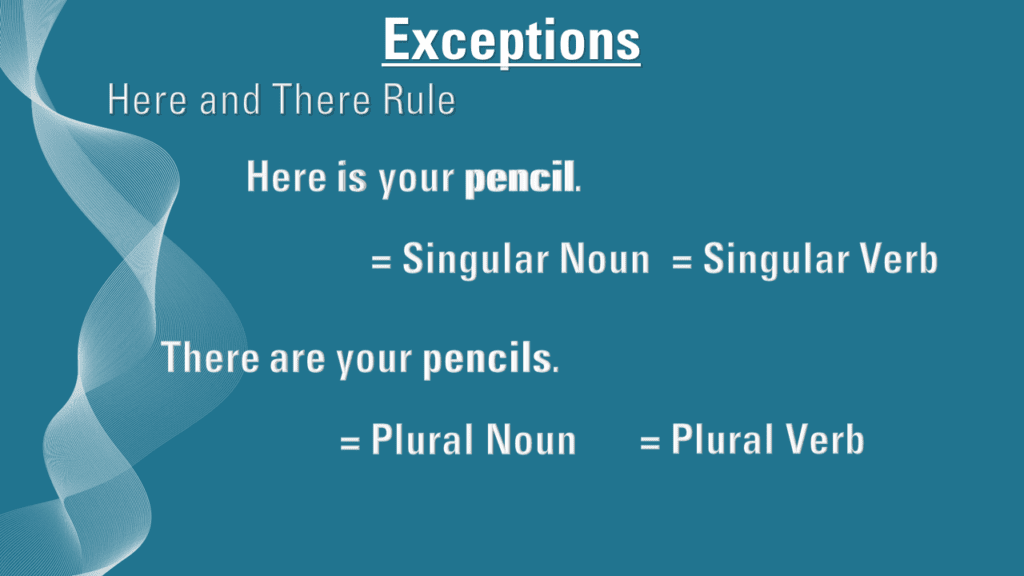
According to this rule, when the subject of the sentence begins with “here” or “there” and is followed by a singular noun, the verb that follows should also be singular. Conversely, when the subject begins with “here” or “there” and is followed by a plural noun, the verb should also be plural.
Let’s look at an example. In this example, the pencil is a singular noun and therefore the verb used after the word here is also a singular verb.
Indefinite Pronouns
Some indefinite pronouns are always singular. Here are some examples: anyone, everyone, someone, no one, nobody.
Others can be either singular or plural (all, some)
Relative Pronouns
Relative Pronouns (who/which/that) can be either singular or plural, depending on the noun they refer to. Let’s take a look at the example.
For more free resources like this, please visit this page.


