FMEA (Failure Mode Effects Analysis) are effective tools for managing and assessing risk to understand and reduce the errors even before they happens. To find probable failures and their effects on goods, processes, and services, FMEA is frequently used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, call centers and automotive.
FMEA is a systematic approach to to find out the risks in the process that helps businesses avoid and reduce failures, improve product quality, and increase customer satisfaction. You can also call FMEA as the proactive approach to defect reduction. This article will cover the basics of FMEA, it’s advantages, benefits and limitations.

What is Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA)?
FMEA is a structured method for determining probable errors in a product, procedure, or service, as well as their effects on stakeholders, users, and customers. Failure Mode Effects Analysis is used to rank failures according to risk categories by determining their likelihood, severity, and priority.
Failure Mode Effects Analysis is a team-based approach that involves cross-functional experts from different departments, such as engineering, quality, production, and maintenance. FMEA is a proactive approach to risk management, as it aims to prevent failures before they occur or mitigate their effects if they do occur.
FMEA can be applied at various stages of the life cycle of a product or process, including design, development, testing, and manufacturing.
The risks connected to external elements, such as environmental dangers, regulatory compliance, and supplier performance, can also be identified using a Failure Mode Impacts Analysis. Several system types, including mechanical, electrical, software, and human aspects, can benefit from FMEA.
Benefits of FMEA:
FMEA provides numerous benefits to organizations that implement it, including:

- Improved product quality: FMEA helps organizations identify potential failure modes and their effects on product quality. By addressing these failures proactively, organizations can improve the quality and reliability of their products, reduce defects, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Cost reduction: Failure Mode Effects Analysis can help organizations save costs by preventing failures that may result in scrap, rework, or warranty claims. FMEA can also help organizations optimize their maintenance schedules and reduce downtime, resulting in cost savings.
- Risk management: FMEA is an effective tool for risk management, as it helps organizations identify, assess, and prioritize risks associated with their products, processes, and services. By addressing high-risk failures proactively, organizations can minimize the likelihood and severity of failures and their effects on customers and stakeholders.
- Continuous improvement: This continuous improvement tool aids businesses in locating areas where their goods, procedures, and services can be improved. Organizations may improve their products and services, learn from mistakes, and implement remedial measures by frequently performing failure mode effects analysis.
- Compliance: It can assist businesses in meeting legal obligations as well as industry standards certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and AS9100.
Steps to Conduct an FMEA:
FMEA typically consists of the following steps:

Step 1: Define the scope and objective of the Failure Mode Effects Analysis
The first step in conducting an failure mode effects analysis is to define the scope and objective of the analysis. This involves identifying the product, process, or service to be analyzed, as well as the purpose of the analysis. The scope of the analysis should be clear and specific to ensure that all relevant failure modes are identified and assessed.
Step 2: Assemble the FMEA team
The second step in conducting an failure mode effects analysis is to assemble the core team that should consist of cross-functional experts from different departments, such as engineering, quality, production, customer services and maintenance. The team members should have the necessary knowledge and skills to identify potential failure modes and their effects.
Step 3: Identify the failure modes

Finding prospective failure modes is the third phase in a failure mode effects analysis. The team should come up with every scenario in which the process, product, or service could go wrong. Many sources, including historical data, customer complaints, supplier feedback, and expert knowledge, can be used to determine the failure modes. The group should use a worksheet or software tool to record the failure modes.
Step 4: Determine the potential effects of the failure modes
Finding the probable repercussions of the failure modes is the fourth stage that you should follow while doing FMEA. The team should determine the effects of each failure mode, such as potential safety risks, poor quality, production loss, and unhappy customers.
The team should also be able categorize each effect’s severity as minor, moderate, or catastrophic. The severity is scaled from 1 to 10, with 10 being the catastrophic. This can be achieved by doing a brainstorming session with each team members.
Step 5: Assign a likelihood rating to each failure mode

Assigning a likelihood rating to each failure mode is the fifth stage in a failure mode effects analysis. Based on the frequency, duration, and detectability of each failure mode, the team should determine how likely it is that it will occur. On a scale of 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest likelihood, the likelihood can be evaluated. This can also be done during the brainstorming session. The team members should not be concentrating on fixing the defects at this point.
Step 6: Calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN)
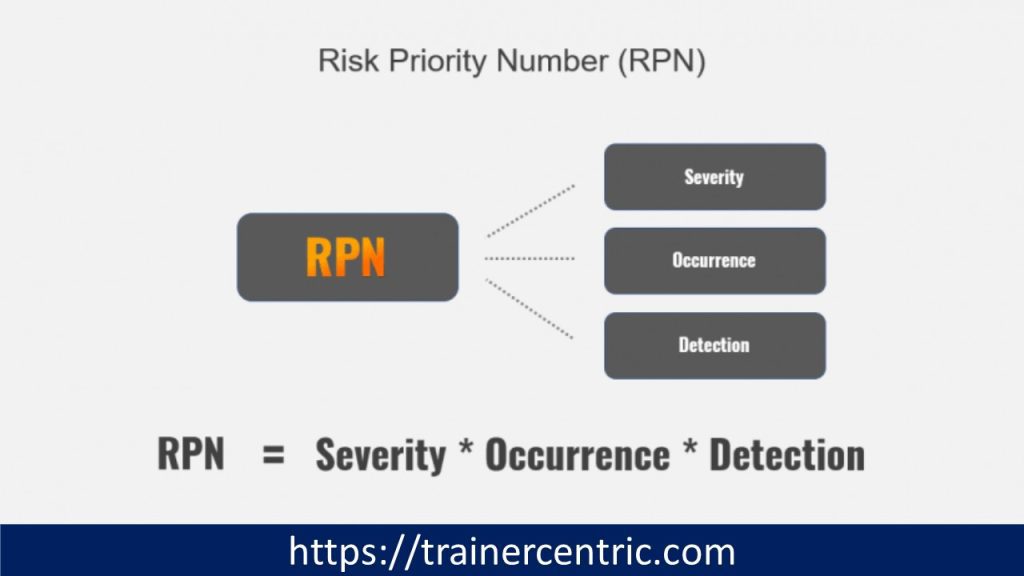
Calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each failure mode is the sixth step in an FMEA. The severity, likelihood, and detectability ratings are combined to create the RPN. The failure modes can be ranked according to their level of risk using the RPN. It is best to start by addressing the failure modes with high RPNs because they present the greatest risks to the final good, process, or service.
Step 7: Identify and implement corrective actions
The identification and implementation of corrective measures to prevent or minimise the high-risk failure modes is the seventh step in performing a Failure Mode Impacts Analysis. To address the reasons of the failure modes, such as design defects, process variations, or human errors, the team should create action plans. To make sure the corrective efforts are working, they should be tracked and documented.
Step 8: Re-assess the FMEA
The eighth step in conducting an FMEA is to re-assess the FMEA after implementing the corrective actions. The team should verify whether the corrective actions have reduced the likelihood and severity of the high-risk failure modes. The team should also update the FMEA worksheet or software tool with the new information and repeat the analysis regularly to ensure continuous improvement.
Conclusion
FMEA is a potent instrument for risk assessment and management that aids businesses in preventing and mitigating failures, enhancing quality, and raising customer satisfaction. Using cross-functional teams, brainstorming, and prioritising high-risk failure modes, FMEA is a proactive method to risk management. Many advantages of FMEA include increased product quality, cost savings, risk management, ongoing improvement, and compliance.
FMEA can be applied to various types of systems and at different stages of the product or process life cycle. By conducting FMEAs regularly and implementing corrective actions, organizations can enhance their products and services, meet customer requirements, and maintain their competitive edge.

![The Power of Storytelling in Corporate Training: Igniting Success and Inspiring Growth [2023]](https://trainercentric.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/storytelling-1024x576.jpg)

